
reduced PCL angle due to buckling of PCL.Segond fracture, and to a lesser degree arcuate sign.uncovered posterior horn of the lateral meniscus.>7 mm of anterior tibial translation, also known as the anterior tibial translocation sign or anterior drawer sign.bone contusion in lateral femoral condyle and posterolateral tibial plateau.footprint sign: incomplete coverage of the lateral aspect of the tibial spine of the tibia by the distal ACL attachment, seen only on coronal MRI images 8.gap sign: fluid signal and/or a gap between the medial aspect of the lateral femoral condyle and the lateral aspect of the mid-ACL, can be seen on either axial or coronal MRI images.Imaging signs of isolated posterolateral bundle tear are as follows: If the angle is still normal and there is a hyperintense signal, a partial rupture is more likely than a complete rupture.ĪCL tear may only involve one bundle. The signal of the ACL can be more hyperintense on T2. empty notch sign: a fluid signal at the site of femoral attachment at the intercondylar notch, denotes avulsion at the femoral attachment.ĪCL tears typically occur in the middle portion of the ligament (midsubstance tears) and appear as discontinuity of the ligament or abnormal contour.ACL angle (angle between the intercondylar line and ACL) >15° with the apex of the angle located anteriorly, indicating a less steep ACL line - this indicates a ruptured and collapsed ligament.ACL fibers are subjectively less steep than a line tangent to the intercondylar roof ( Blumensaat's line).
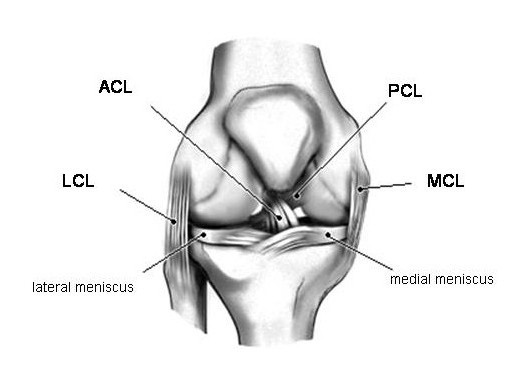

Primary signs are those that pertain to the ligament itself. Imaging of anterior cruciate ligament tears should be divided into primary and secondary signs. CT helps characterize the avulsion bone fragment when it is present.
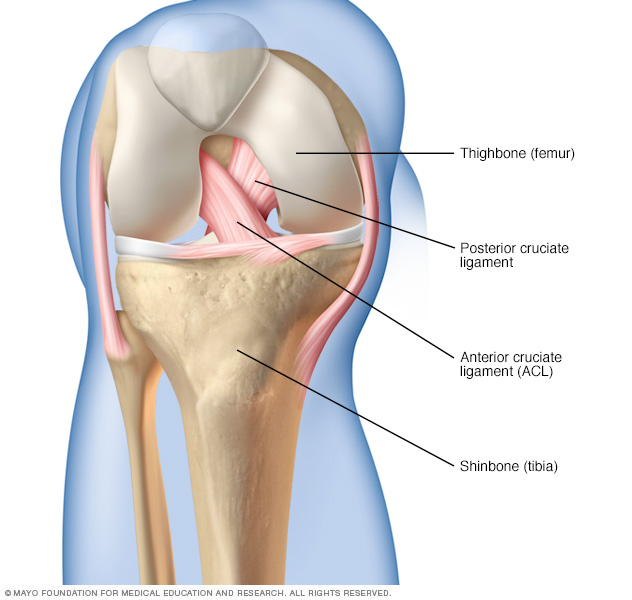
The combination of the Lachman, pivot shift and anterior drawer tests are used to clinically confirm diagnosis 9. apprehension with an attempt at non-linear movements.knee felt to "gives way" especially during pivoting movement.initial inability to weight bear, which improves in a short period.popping sensation at the time of injury, followed by swelling.The following signs and symptoms are common: Patients typically present with symptoms of knee instability, usually after acute trauma.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
